
Finally, it cannot model complex dependency and uncertainty.Ĭrude oils and fats limits are set for pesticides, hydrocarbons of mineral origin, and previous cargoes. Secondly, it is often found oversimplified which cannot capture the detail process risk profile. Firstly, it is a user perspective approach the same matrix can be interpreted differently by another user unless each condition is clearly described. However, there are several significant disadvantages, as well. The major advantage of the risk matrix is that it allows representing complex risk data in a compressed form. Qualitative outcomes are separated from each other by distinct colors which make it easier to visualize. 4 shows an illustrative risk matrix where the probability of failure is shown on the vertical axis, and the severity of consequences is displayed on the horizontal axis. However, if both the fundamentals of risk: the probability of failure and severity of consequences are expressed in a qualitative manner, the risk matrix becomes a purely qualitative approach. The risk matrix has been described as a semi-quantitative approach by many scholars ( Ni, Chen, & Chen, 2010 Ruge, 2004).
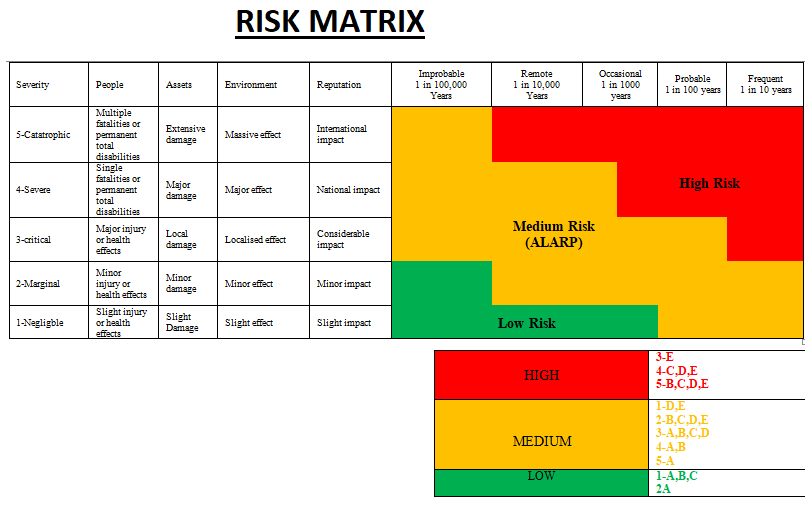
Since its inception, the risk matrix has become one of the most widely used qualitative risk assessment technique that has been well adopted by the industries for its simplicity, yet, effectiveness. The idea of a risk matrix was first developed in the Electronic System Centre, US Air force ( Garvey & Lansdowne, 1998). Any higher frequency would require the HAZOP team to formally recommend the installation of additional IPLs.

According to the sample risk matrix selected for this analysis ( Table 13.1), a category 5 incident requires a frequency of consequence of 1 × 10 −6 years or less to achieve an acceptable level of risk tolerance (no further action required). In order for process design to meet risk tolerance criteria, it must include sufficient IPLs to reduce the frequency of consequence down to a degree that requires no further action. In fact, any scenario ending with the escape of MIC gas to the atmosphere would probably qualify for the most severe category on any risk matrix, regardless of how many consequence categories are defined. For this reason, the HAZOP team would likely assign a category 5 consequence to any scenario involving the release of MIC gas into the atmosphere. Doing so might produce toxic inhalation effects that could realistically produce the highest consequence possible. Simply stated, gaseous MIC could not be safely released into the atmosphere. However, there should be no argument over the consequence level represented by any scenario involving the release of hot MIC gas into the atmosphere. Some companies may assign more than five consequence categories, depending on how they define their consequence thresholds. The example risk matrix consequence categories ( Table 13.1) range from one to five, with five being the highest possible consequence (a fatality). Kenneth Bloch, in Rethinking Bhopal, 2016 Consequence Category Property (including plant): Plant damage value in the range of say, $0.1–1.0M units of currency Onsite: Potential for injuries requires only first aidĮnvironmental: Contained release with local impact only Property (including plant): Plant damage value in the range of say, $1–10M units of currency
Onsite/offsite: Potential for an injury requires medical attentionĮnvironmental: Uncontained release with potential for minor environmental impact Property (including plant): Plant damage value in the range of say, $10–100M units of currency Onsite/offsite: Potential for single life-threatening injury or fatalitiesĮnvironmental: Uncontained release with potential for moderate environmental impact Property (including plant): Plant damage value in excess of say, $100M units of currency. Onsite/offsite: Potential for multiple life threatening injury or fatalitiesĮnvironmental: Uncontained release with potential for major environmental impact


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
